Published 18 March 2022 – ID G00761512 – 5 min readBy Matt Cain, Christopher Trueman
While the exact evolution and end state of the metaverse is unclear, metaverse-related dynamics will have a profound impact on the digital employee experience throughout the decade, making it relevant to application leaders supporting the digital workplace.
Quick Answer
How will the metaverse shape the digital employee experience?
While most of the metaverse1 hullabaloo is about consumer experiences, it — like other stages of internet development — will have a profound impact on the digital employee experience. Through 2030, metaverse trends will impact employees via: Relationships with partners, suppliers and customers: the internet underpins most employee interactions with external parties, and as the internet evolves into the metaverse, those interactions will change.
- More transactions will be initiated by digital customers and will use digital currencies and distributed ledger technologies.
- More human interactions will use avatars and more physical navigation will be through virtual landscapes.
- Sensors will collect vastly more data from equipment and activities — fueling the rise of digital twins — and the physical world will be augmented with data overlays — via the spatial web — creating immersive relationships.
Job skills: As the technological underpinnings of the metaverse evolve, so will the job skills needed to build, support and navigate the metaverse. Few, if any, jobs will be left untouched by metaverse technologies, just as few jobs were left unaffected by earlier internet developments.
- Creatives will need augmented and virtual reality skills.
- Support personnel will resolve issues with immersive technologies.
- IT will support new metaverse hardware and infrastructure, security will support biometric identities, application developers will need AR/VR skills.
- Finance will support Web3 services.
- Sales people will sell in virtual showrooms and spaces.
- Marketing will spend the majority of its budget in metaverse properties.
Internal operations: As metaverse elements propagate across the internet, organizations will create their own “intraverse” to host internal operations.
- Many activities — including learning, procurement, onboarding and live events — will occur in virtual spaces.
- Metaverse technologies will shift collaboration activities to avatars navigating virtual meeting rooms and conference spaces, recreating the immersive experience of in-person interactions.
- The physical office space will have virtual overlays to help employees navigate, understand and optimize the space.
More Detail
The good news is that the metaverse does not require any specific action on the part of digital workplace leaders at present. The most immediate impact will be on meeting technology, which will become increasingly immersive.The evolution of the intranet into the intraverse will soon follow. Immersive technologies — in use today — will accelerate, particularly in areas such as learning, events and field support.Therefore the immediate need is for digital workplace leaders to understand and be able to explain basic concepts about the evolution and importance of the metaverse to business leaders and put these in the context of their impact on the workforce. The question of “what are we doing about the metaverse” is bound to increase, and digital leaders should be able to explain where metaverse technologies are deployed and planned, and help others to be alive to the myriad internal and external possibilities of metaverse technologies.These are the most important dynamics to keep in mind when assessing the impact of the metaverse on the digital employee experience:
The Metaverse Is Evolutionary, Not Revolutionary
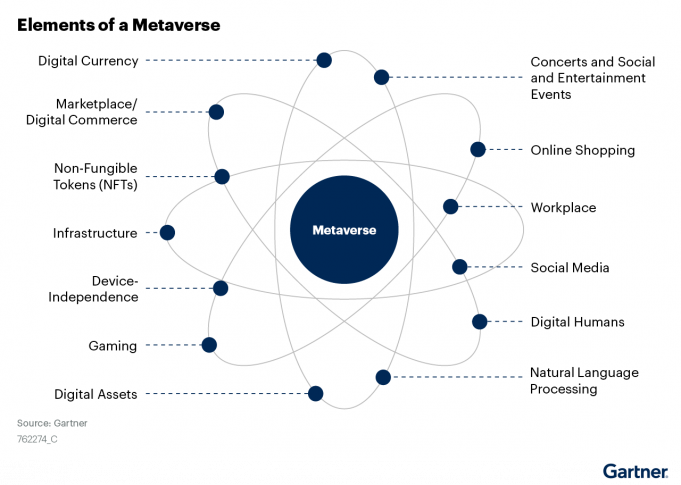
Media attention about the metaverse through the end of 2022 is likely to continue to be sensational, leading many to conclude that a digital revolution is imminent. The reality is that the metaverse represents the continuing evolution of the internet and how it is used. People are spending more time online and are conducting more business online, much of which is occurring in what might be called precursor metaverse sites. More commerce is occurring through digital currencies and with distributed ledger technologies. Use of avatars, purchase of digital products and attendance at virtual events are becoming mainstream. The metaverse is a coalescence of these trends, where the physical and the virtual become increasingly intertwined.
The Metaverse Will Have ‘Consumer’ and ‘Industrial’ Orientations
In the consumer orientation, ‘follow the money’ is a reasonable way to understand the role the metaverse will play. Any large consumer facing web property will use the metaverse to help sell more things, including ads, entertainment, consumer goods, games and experiences. The longer a customer is engaged (and immersed) on a site, the more opportunity there is for sales. The industrial orientation, conversely, will be driven by the quest for greater efficiencies in operations. IoT, edge computing and spatial computing will combine to vastly increase the ability to collect and process data and mix physical and virtual elements to understand and optimize industrial material handling, manufacturing and service operations.
The Metaverse Is an Example of Combinatorial Innovation
Combinatorial innovation is the creation of new things through the mashup of disparate technologies.Thousands of technologies will underpin the metaverse. Some of the most important pillars will be:
- Faster and more granular networking via 5G.
- Graph databases for entity relationships.
- Digital-spatial anchors to recognize things in the physical world and link them to contextually relevant data.
- Computer vision for machines to recognize and interact with physical objects.
- Natural language processing for text and verbal interactions with metaverse components.
- Virtual assistants to act as helpers and agents in navigating the metaverse.
- digital currencies for financial transactions.
The Metaverse Will Develop in Three Stages.
The metaverse will develop through three overlapping stages from 2022 through the early 2030s.Characteristics of each stage will include:
- Emerging (early 2020s). Most use cases are around the kind of virtual reality experiences often found in gaming, for example. There is no interoperability across “miniverses.” Access is via a limited set of devices, there is little connection to the physical world, and sporadic use of digital currency and assets.
- Advanced (mid 2020s). Protocols start to emerge to facilitate interoperability across miniverses, digital humans and digital twins, along with digital currencies and assets becoming common. Edge computing and physical environmental mapping create more points of intersection between the physical and digital worlds.
- Mature (late 2020s through early 2030s). Most of the physical world — via “spatial computing” has been mapped and indexed, allowing deep integration of the physical and digital worlds. Interoperability across miniverses is common, device independence and multiexperience (interaction via voice, for example) is expected. Virtual assistants are deeply intertwined into everyday experiences.
Recommended by the Authors
Quick Answer: What Is a Metaverse?Emerging Technologies: Critical Insights on MetaverseQuick Answer: How to Increase Customer Engagement and Drive Revenue in the MetaverseAugmented Reality and Virtual Reality Will Transform SellingThe Virtuous Circle of Collaboration With Augmented Reality in Field ServiceQuick Answer: How to Use Combinatorial Innovation to Identify Opportunities From Trends and Emerging TechnologiesEmerging Technologies: The Future of the Metaverse
Evidence
1 Gartner defines a metaverse as, “A collective virtual shared space, created by the convergence of virtually enhanced physical and digital reality. A metaverse is persistent, providing enhanced immersive experiences.” Gartner expects that a complete metaverse will be device-independent and will not be owned by a single vendor: It will have a virtual economy of itself, enabled by digital currencies and nonfungible tokens (NFTs).